
An SEO audit is a comprehensive evaluation of a website’s search engine optimization (SEO) performance. The purpose of an SEO audit is to identify areas where a website may be falling short in terms of SEO best practices and to provide actionable recommendations to improve its visibility in search engine results.
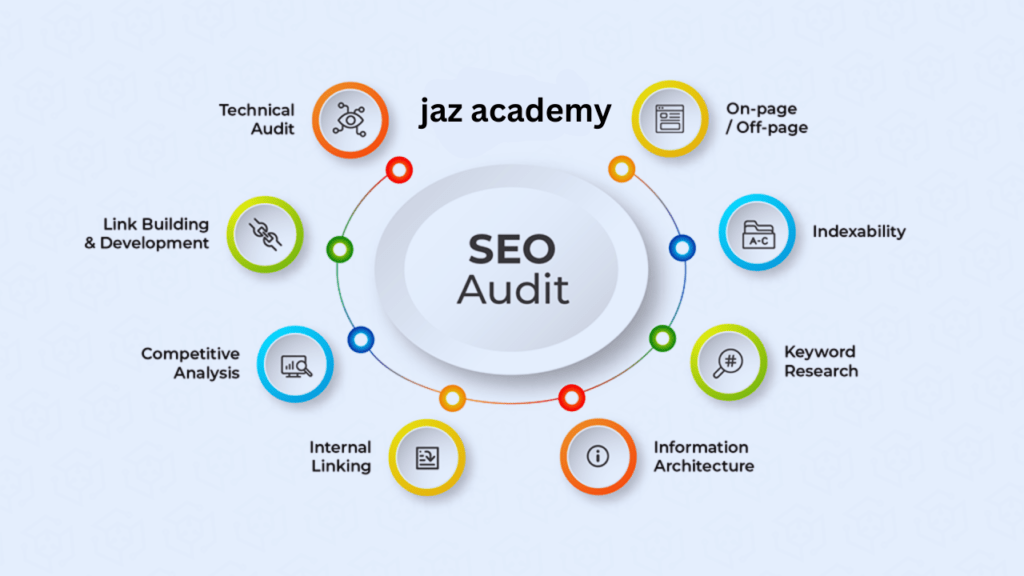
Key Components of an SEO Audit
Technical SEO Analysis:
Site Crawlability: Check if search engines can crawl your site effectively. This involves examining robots.txt files, XML sitemaps, and crawl errors.
Indexability: Ensure that pages are indexed correctly and identify any issues like “noindex” tags or canonical tag misconfigurations.
Site Speed: Analyze page load times and identify factors that may be slowing down the site, such as large images or inefficient code.
Mobile-Friendliness: Evaluate the site’s mobile responsiveness and usability on various devices.
HTTPS: Confirm that the site uses HTTPS to ensure secure connections.
On-Page SEO Review:
Content Quality: Assess the relevance, originality, and quality of the content on the site.
Keyword Optimization: Review how well keywords are incorporated into page titles, meta descriptions, headers, and body content.
Meta Tags: Check if meta titles and descriptions are optimized and unique for each page.
Internal Linking: Evaluate the effectiveness of internal linking structure and whether it supports good navigation and page authority distribution.
Image Optimization: Ensure images have descriptive alt tags and are optimized for speed.
Off-Page SEO Evaluation:
Backlink Profile: Analyze the quantity and quality of backlinks pointing to the site. Identify any toxic links that could harm your SEO.
Social Signals: Examine the site’s social media presence and how it influences SEO.
User Experience (UX) and Design:
Site Navigation: Assess the ease of navigation and overall user experience. Ensure that users can find information quickly and easily.
Mobile Usability: Verify that the site is easy to use on mobile devices.
Competitor Analysis:
Benchmarking: Compare your site’s SEO performance against competitors to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Opportunities: Identify gaps and opportunities where your site can outperform competitors.
Analytics and Reporting:
Traffic Analysis: Use tools like Google Analytics to analyze traffic patterns, user behavior, and conversion rates.
SEO Metrics: Track key SEO metrics such as organic search traffic, keyword rankings, and click-through rates (CTR).
Steps to Perform an SEO Audit
Define Objectives: Understand the goals of the audit, whether it’s to improve rankings, increase traffic, or resolve specific issues.
Collect Data: Use various tools (e.g., Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs) to gather data on technical aspects, content, and backlinks.
Analyze Data: Review the data to identify issues and opportunities in the areas mentioned above.
Prioritize Issues: Based on the analysis, prioritize issues according to their impact on SEO performance and create a plan for addressing them.
Develop an Action Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps needed to resolve identified issues and improve SEO.
Implement Recommendations: Take action on the recommendations provided in the audit, making necessary changes to the website.
Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor the site’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review the site to ensure ongoing compliance with SEO best practices.
How to Perform an Audit for SEO
The process of assessing a website’s search engine optimization and pinpointing areas in need of development is called an SEO audit. The steps to carry out an SEO audit are as follows, according SEMrush:
1. Establish Objectives
Establishing the audit’s goals and objectives is the first stage in performing an SEO audit. The target audience for the website, key performance indicators (KPIs), and areas in need of improvement are all part of this process.
2. Assess the architecture of the site
Assessing the design and structure of the website is the second step in performing an SEO audit. Analyzing the website’s internal linking structure, navigation, speed, and URLs is part of this process.
3. Analyze On-Page Optimization
Analyzing the website’s on-page optimization is the third step in performing an SEO audit. Assessing the website’s content, headings, titles, meta descriptions, and images for optimization and relevancy falls under this category.
4. Check for Indexing Issues
Examining problems with indexation is the fourth stage in an SEO audit. Finding duplicate material, broken links, and crawl problems that may have an impact on a website’s search engine rankings is part of this.
5. Analyze Backlink Profile
Analyzing the backlink profile of the website is the fifth stage in performing an SEO audit. This entails assessing the backlink profile, relevancy, and variety of the website.
6. Monitor User Experience
Monitoring user experience is the sixth step in performing an SEO audit. To find opportunities for improvement, this involves examining the website’s bounce rate, user engagement, and user behavior.
7. Use SEO Audit Tools
It’s crucial to assess the website’s performance and pinpoint areas for improvement using SEO audit tools like SEOptimer or SEMrush.
8. Take Action
It’s important to act and put the suggested adjustments into practice after finishing an SEO audit. This includes improving the website’s architecture and structure, constructing high-quality backlinks, and optimizing the content to raise its search engine ranks.
Conclusion
An SEO audit is a critical process for evaluating and enhancing a website’s SEO performance. By systematically examining technical aspects, on-page elements, off-page factors, and user experience, an SEO audit provides valuable insights and actionable recommendations. Addressing the findings from an audit helps improve search engine visibility, user experience, and overall site performance, contributing to better rankings and increased organic traffic.






0 Comments